Brain damage and traumatic brain injuries in newborns can sometimes be detected by physical appearances, recognized through brain scans, a child’s disposition, or developmental delays. Not all brain damages exhibit physical abnormalities but those that do often have unusually shaped skull structures (quite often a tiny skull size), difficulty focusing the eyes, large forehead, deformed spine, and other facial abnormalities.
Identifying Brain Injuries through Behavioral and Developmental Characteristics
 Behavioral differences include excessive fussiness, extended periods of crying, refusal to sleep lying down, or too much or too little sleep. Another common indicator of brain damage is developmental delays. There are typical milestones that are generally expected of young children at specific stages of their life. For instance, there is a general age when most infants begin crawling, rolling over, uttering their first word, and so forth. A child with brain damage may have difficulty reaching these milestones at the typical age. Other symptoms can include body temperature, skin color, breathing patterns, seizures, and other similar indicators.
Behavioral differences include excessive fussiness, extended periods of crying, refusal to sleep lying down, or too much or too little sleep. Another common indicator of brain damage is developmental delays. There are typical milestones that are generally expected of young children at specific stages of their life. For instance, there is a general age when most infants begin crawling, rolling over, uttering their first word, and so forth. A child with brain damage may have difficulty reaching these milestones at the typical age. Other symptoms can include body temperature, skin color, breathing patterns, seizures, and other similar indicators.
If your newborn baby suffers from one of the mentioned symptoms, it does not necessarily mean that your baby has brain damage or has suffered a traumatic brain injury. Abnormalities can occur due to wide array of reasons. Brain damage can only be diagnosed by a well-qualified and specialized medical professional. Each individual case varies depending on many factors. Your physician will know your specific situation better than anybody else and he or she will be able to identify any issues your child may be experiencing both externally and internally.
Traumatic Brain Injuries Lawyers in New Jersey and Philadelphia
Traumatic brain injuries that have caused brain damage can be very detrimental to the health of a young child and it is crucial to identify potential problems as early as possible. If your child has suffered from some sort of brain damage and you believe the problem has been worsened by ineffective medical treatment it is likely you have some questions. Please contact the Mininno Law Office for a free case evaluation or call for a free consultation at (856) 833-0600 in New Jersey, or (215) 567-2380 in Philadelphia.
 Brain damage can be categorized in one of two ways – acquired and traumatic. Acquired brain injuries are those that do not result from external forces. For example, a stroke would cause an acquired brain injury because no outside forces are the cause. Depending on the site of the lesions ( a lesion is any area of tissue or organ that has suffered damage) and severity of the stroke, the brain damage can affect the victim in different ways. Traumatic brain injury is damage that is caused by external forces. A motor vehicle accident, known as MVA to medical professionals, is often the cause of traumatic brain injuries.
Brain damage can be categorized in one of two ways – acquired and traumatic. Acquired brain injuries are those that do not result from external forces. For example, a stroke would cause an acquired brain injury because no outside forces are the cause. Depending on the site of the lesions ( a lesion is any area of tissue or organ that has suffered damage) and severity of the stroke, the brain damage can affect the victim in different ways. Traumatic brain injury is damage that is caused by external forces. A motor vehicle accident, known as MVA to medical professionals, is often the cause of traumatic brain injuries.  The study gave imipramine, a commonly prescribed antidepressant, to injured lab mice. Researcher, Dr. Jason Huang, associate professor of neurosurgery at the University of Rochester Medical Center and chief of neurosurgery at Highland Hospital in New York, found that the mice treated with imipramine showed 70% more brain cell growth than the mice that were not treated with the drug. In addition to cell growth, the treated mice also displayed, through behavioral testing, improved memory skills.
The study gave imipramine, a commonly prescribed antidepressant, to injured lab mice. Researcher, Dr. Jason Huang, associate professor of neurosurgery at the University of Rochester Medical Center and chief of neurosurgery at Highland Hospital in New York, found that the mice treated with imipramine showed 70% more brain cell growth than the mice that were not treated with the drug. In addition to cell growth, the treated mice also displayed, through behavioral testing, improved memory skills.  Liu, now 29, was struck in 2007 by 67 year old Douglas Wayne Seybert as he was turning an “S” curve on the Freeport Boulevard in Sacramento. Liu’s traumatic injury case focused on the lack of visibility along the boulevard where she was struck. Liu’s attorney argued that the city was negligent in providing substantial warning to motorists about the crosswalk they are approaching, the same crosswalk where Liu was hit.
Liu, now 29, was struck in 2007 by 67 year old Douglas Wayne Seybert as he was turning an “S” curve on the Freeport Boulevard in Sacramento. Liu’s traumatic injury case focused on the lack of visibility along the boulevard where she was struck. Liu’s attorney argued that the city was negligent in providing substantial warning to motorists about the crosswalk they are approaching, the same crosswalk where Liu was hit. 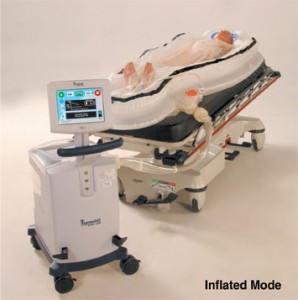 The treatment is called therapeutic hypothermia, and it is relatively new in the medical field. Therapeutic hypothermia involves lowering an unconscious patient’s temperature to between 32 and 34 degrees celsius using a “cooling blanket,” a special cap, or a mattress filled with either air or liquid. The aim of the treatment is to cool the patient’s brain and slow the rate of cell damage, therefore preventing irreversible brain injury or damage.
The treatment is called therapeutic hypothermia, and it is relatively new in the medical field. Therapeutic hypothermia involves lowering an unconscious patient’s temperature to between 32 and 34 degrees celsius using a “cooling blanket,” a special cap, or a mattress filled with either air or liquid. The aim of the treatment is to cool the patient’s brain and slow the rate of cell damage, therefore preventing irreversible brain injury or damage.  Military healthcare officials are collectively refusing to pay for a new treatment to rehabilitate
Military healthcare officials are collectively refusing to pay for a new treatment to rehabilitate 



